

Automated QA testing runs alongside the software development lifecycle and includes the stages below:
The first step involves a feasibility analysis and figuring out the aims of the testing process while considering factors such as budget, expertise, and resources.
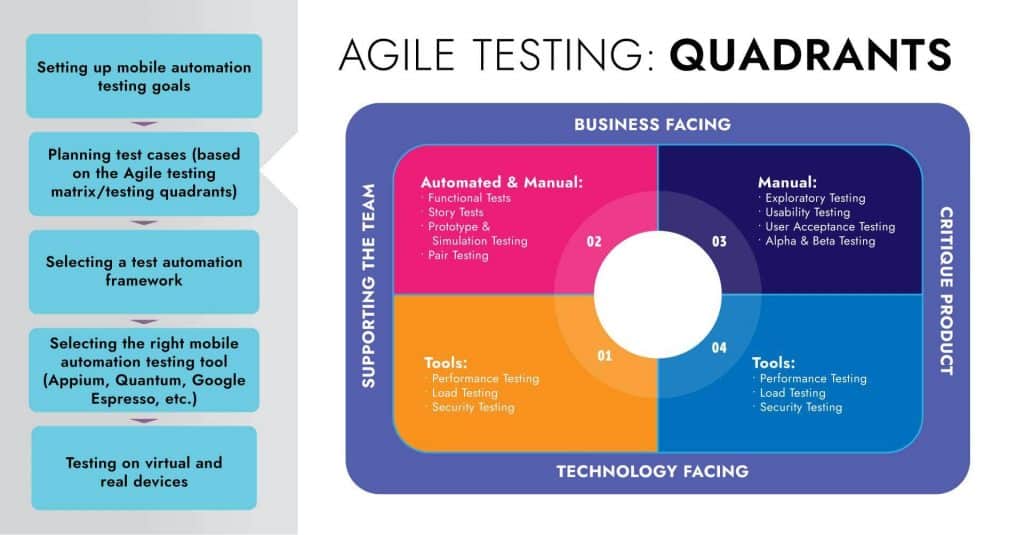
After defining the scope of the test, choose an automation tool that fits the project requirements. Factoring in the tool’s cost, along with flexibility, functionality, and intuitiveness is equally critical.
Next, the QA team must design a suitable testing framework that aligns with the project’s approach and end goals and contains common practices, standards, and testing tools.
Creating the proper testing environment is crucial to maximising test coverage. For this, the QA team must develop testbed scripts, schedule and track hardware and software installation, along with other environment setup activities.
In this step, the QA team writes automated test scripts to run the tests. The scripts must be structured, reusable, easy-to-understand, and based on scripting standards and project requirements.
API testing and GUI testing are the two main ways to automate QA tests. Different software tests include unit tests, functional tests, integration tests, end-to-end tests, smoke tests, regression tests, and performance tests.
After the test execution, the automation tool will generate a report showing errors or if additional testing is required.
Manual testing is error-prone, even if done by the most diligent tester. Automation testing improves accuracy and frees testers from repetitive manual tests.
With automated testing, whenever there is a change in the source code, tests can run automatically. Thus, developers can identify problems on the fly, which, in turn, saves time and resources.
Automation testing simplifies and improves the detection of bugs and other defects. Moreover, automation testing can perform controlled web application tests with thousands of virtual users.
Automation significantly increases testing speed, shortens software development cycles, facilitates frequent releases, enables quicker updates to the app, and ensures faster time-to-market delivery.
Automated testing is the key to implementing DevOps practices and switching to the continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 1 hour | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| _cfuvid | session | Calendly sets this cookie to track users across sessions to optimize user experience by maintaining session consistency and providing personalized services |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie records the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | CookieYes sets this cookie to record the default button state of the corresponding category and the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| wpEmojiSettingsSupports | session | WordPress sets this cookie when a user interacts with emojis on a WordPress site. It helps determine if the user's browser can display emojis properly. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| li_gc | 6 months | Linkedin set this cookie for storing visitor's consent regarding using cookies for non-essential purposes. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| wp-wpml_current_language | session | WordPress multilingual plugin sets this cookie to store the current language/language settings. |
| yt-remote-cast-installed | session | The yt-remote-cast-installed cookie is used to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-fast-check-period | session | The yt-remote-fast-check-period cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences for embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-session-app | session | The yt-remote-session-app cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences and information about the interface of the embedded YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-session-name | session | The yt-remote-session-name cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY | never | The cookie ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY is used by YouTube to store the last search result entry that was clicked by the user. This information is used to improve the user experience by providing more relevant search results in the future. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to calculate visitor, session and campaign data and track site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognise unique visitors. |
| _ga_* | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store and count page views. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Google Tag Manager sets the cookie to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _li_id | 2 year | Leadinfo places two cookies that only provides Eastern Enterprise insights into the behaviour on the website. These cookies will not be shared with other parties. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bcookie | 1 year | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser IDs. |
| guest_id | 1 year 1 month | Twitter sets this cookie to identify and track the website visitor. It registers if a user is signed in to the Twitter platform and collects information about ad preferences. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | doubleclick.net sets this cookie to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to measure bandwidth, determining whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| VISITOR_PRIVACY_METADATA | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's cookie consent state for the current domain. |
| YSC | session | Youtube sets this cookie to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __Secure-ROLLOUT_TOKEN | 6 months | Description is currently not available. |

