
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to cloud computing. An organization must determine the cloud computing architecture or the type of cloud deployment best suited for its cloud services. Broadly, there are three dierent models for deploying cloud services: on a private cloud, public cloud, or hybrid cloud.
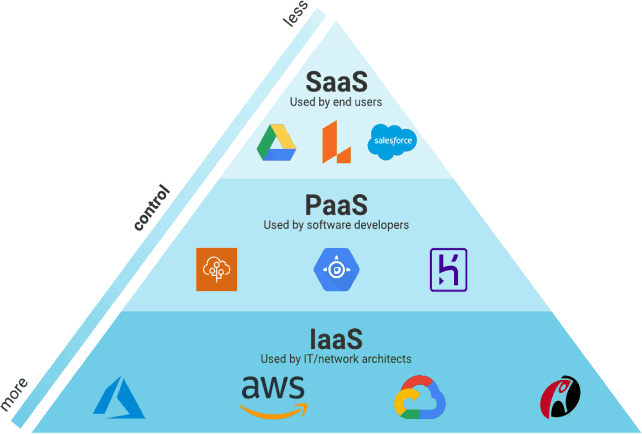
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
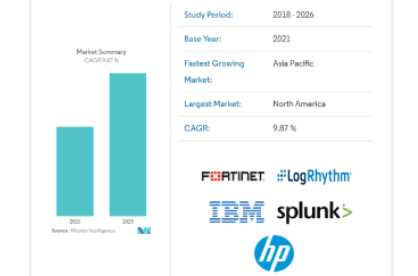
Backed by AI-driven technologies, SIEM offers a complete security orchestration solution to enable IT teams to automate threat monitoring, detection, and response.
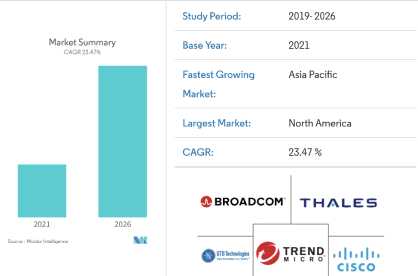
DLP services offer tools and solutions to ensure regulated cloud data security. The growth of the global DLP market has been fueled by the growing need for organizations to meet data regulatory and compliance requirements.
IAM services and tools allow the deployment of policy-driven enforcement protocols for both cloud-based and on-premise service users. IAM solutions can actively monitor and restrict users during data interactions by creating digital identities for all users.
Disaster recovery solutions are a cloud security fundamental that provides the protocols, tools, and services necessary to accelerate the recovery of lost data and ensure business continuity.
Cloud computing has significant advantages when compared to traditional on-premise data centres.
Shifting to cloud computing solutions can relieve organizations from bearing additional expenses of operating and managing on-premise data centres.
Cloud computing enables automation of elaborate processes, such as hardware setup and regular software patching, allowing IT teams to invest resources into more essential business aspects.
With cloud computing, enterprises can quickly and easily access a host of IT resources within the cloud, including storage, servers, databases, software, networking, intelligence, and analytics.
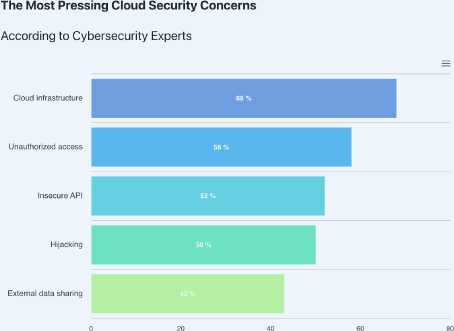
Cloud security solutions offer a range of tools and technologies to help strengthen the security ecosystem of organizations from potential threats, ensuring cost-effective data backup and disaster recovery.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 1 hour | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| _cfuvid | session | Calendly sets this cookie to track users across sessions to optimize user experience by maintaining session consistency and providing personalized services |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie records the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | CookieYes sets this cookie to record the default button state of the corresponding category and the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| wpEmojiSettingsSupports | session | WordPress sets this cookie when a user interacts with emojis on a WordPress site. It helps determine if the user's browser can display emojis properly. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| li_gc | 6 months | Linkedin set this cookie for storing visitor's consent regarding using cookies for non-essential purposes. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| wp-wpml_current_language | session | WordPress multilingual plugin sets this cookie to store the current language/language settings. |
| yt-remote-cast-installed | session | The yt-remote-cast-installed cookie is used to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-fast-check-period | session | The yt-remote-fast-check-period cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences for embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-session-app | session | The yt-remote-session-app cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences and information about the interface of the embedded YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-session-name | session | The yt-remote-session-name cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY | never | The cookie ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY is used by YouTube to store the last search result entry that was clicked by the user. This information is used to improve the user experience by providing more relevant search results in the future. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to calculate visitor, session and campaign data and track site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognise unique visitors. |
| _ga_* | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store and count page views. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Google Tag Manager sets the cookie to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _li_id | 2 year | Leadinfo places two cookies that only provides Eastern Enterprise insights into the behaviour on the website. These cookies will not be shared with other parties. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bcookie | 1 year | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser IDs. |
| guest_id | 1 year 1 month | Twitter sets this cookie to identify and track the website visitor. It registers if a user is signed in to the Twitter platform and collects information about ad preferences. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | doubleclick.net sets this cookie to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to measure bandwidth, determining whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| VISITOR_PRIVACY_METADATA | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's cookie consent state for the current domain. |
| YSC | session | Youtube sets this cookie to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __Secure-ROLLOUT_TOKEN | 6 months | Description is currently not available. |

